| Pacific Electric Connects Southern California Cities
 In
the area surrounding Los Angeles a number of cities grew creating the need for fast and economical transportation between
these cities. In 1901 Henry Huntington purchased the line between Pasadena and Los Angeles and started building the Pacific Electric
interurban railway network which allowed people to live in the outlying cities and developing suburbs while working and transacting
business in the central city. In
the area surrounding Los Angeles a number of cities grew creating the need for fast and economical transportation between
these cities. In 1901 Henry Huntington purchased the line between Pasadena and Los Angeles and started building the Pacific Electric
interurban railway network which allowed people to live in the outlying cities and developing suburbs while working and transacting
business in the central city.
Pacific Electric Railway Company was incorporated by Henry Huntington on November 10, 1901. Pacific Electric took
over the financially troubled Los Angeles-Pasadena interurban line, then built a new line, between Los Angeles and Long Beach,
which opened on July 4, 1902.
During its first decade, lines were completed to to Monrovia, Glendora, Sierra Madre, Newport Beach, San Pedro and Santa
Ana.
In 1911, Southern Pacific bought out Huntington, except for the
LARy, and also purchased several other passenger railways Huntington owned in the Los Angeles area, resulting in the "Great
Merger" of 1911.
By 1914, one could also go from downtown L.A. to San Bernardino or San Fernando.
Pacific Electric also offered low cost trips to a variety of southern California destinations.
 The Pacific Electric also operated the Mount Lowe Railway, a scenic mountain railroad created
as a tourist attraction on Echo Mountain and Mount Lowe, at the crest of the San Gabriel Mountains, north of Pasadena. Originally
built by Professor Thaddeus S. C. Lowe, the line opened in 1893 and was nearly seven miles long. The railway started in Altadena, climbed Lake
Avenue and crossed the Poppyfields into the Rubio Canyon. From there passengers transferred
to a cable car funicular which
climbed the Great Incline to the top of the Echo Mountain promontory, the location of two hotels, an astronomical observatory,
car barns, dormitories and repair facilities, a casino and dance hall. Passengers
could transfer to another trolley line which would take them to the upper terminus at Crystal Springs
and Ye Alpine Tavern. The Pacific Electric also operated the Mount Lowe Railway, a scenic mountain railroad created
as a tourist attraction on Echo Mountain and Mount Lowe, at the crest of the San Gabriel Mountains, north of Pasadena. Originally
built by Professor Thaddeus S. C. Lowe, the line opened in 1893 and was nearly seven miles long. The railway started in Altadena, climbed Lake
Avenue and crossed the Poppyfields into the Rubio Canyon. From there passengers transferred
to a cable car funicular which
climbed the Great Incline to the top of the Echo Mountain promontory, the location of two hotels, an astronomical observatory,
car barns, dormitories and repair facilities, a casino and dance hall. Passengers
could transfer to another trolley line which would take them to the upper terminus at Crystal Springs
and Ye Alpine Tavern.
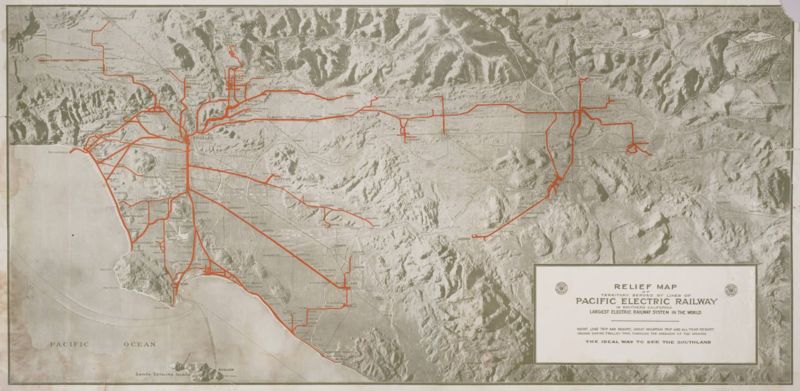
The Pacific Electric grew to become the largest interurban system in the world, spanned 1,100
miles, operating 1,200 cars throughout Southern California and was the primary means of transportation
in the pre-freeway age. The PE provided fast efficient passenger and freight interurban transportation
Los Angeles, Orange, San Bernardino and Riverside Counties, making commuting within minutes possible.
Suburban towns sprang up and developed along the PE rails. The Pacific Electric also ran one of the few electrically-powered
Railway Post Office routes in the country.
Throughout most of its existence, the PE divided itself into three main
divisions for ease and efficiency of operation.
- The Northern District was the largest throughout most of its history, totaling
approximately 400 miles of trackage divided into 33 separate lines. Lines included the Los
Angeles Terminal District, Pasadena Short Line, Pasadena Oak Knoll Line, Pasadena Local Lines,
Sierra Madre Line, Monrovia - Glendora Line, Mount Lowe Line, Alhambra - San Gabriel Line,
South Pasadena Lines, San Bernardino Line, Pomona Local Lines, Ontario & San Antonio Heights
Line, Pomona - Claremont Pomona - Upland Line. San Bernardino Local Lines, San Dimas Local
Line, Arrowhead Line, Highland Line, Riverside - Redlands Line, San Bernardino - Riverside
Line, Redlands Local Lines, Riverside Local Lines, Riverside - Corona Line and the Riverside
- Rialto Line.
- The Southern District included the Four Tracks, Gardena-San Pedro, Hawthorne
Branch, Santa Ana-Huntington Beach Line, San Pedro via Dominguez, La Habra-Fullerton Line,
Catalina Specials, Watts Local Line, Torrance Line, the busy Long Beach-San Pedro Line, the
seaside Newport-Balboa Line and the Santa Ana-Orange Line.
- The Western District comprised the network of lines formerly belonging to
the Los Angeles Pacific Company plus several other lines. Lines included the Hollywood Subway,
Sherman - West Hollywood Line, West Sixteenth Street Line, Venice Short Line, Santa Monica
via Sawtelle Line, Westgate Line, Santa Monica Local Lines, Redondo Beach - Del Rey Line, Lagoon
Line, Coldwater Canyon Line, Santa Monica Canyon Line, Cahuenga Valley Line, Quint Cutoff,
Sherman Cutoff, Santa Monica Air Line, Inglewood Line, Hollywood Lines, South Hollywood - Sherman
Line, Western & Franklin Line, Echo Park Avenue Line, San Fernando Valley Line, Glendale
- Burbank Line, Edendale Line. As of December, 1916, the Western District totaled 260 miles
of trackage, divided into 12 lines over which operated 395 trains each day comprised of 566
cars.
 During the 1920s the popularity of automobiles increased and service to some communities was discontinued. Increasing automobile
traffic also led to decreasing Red Car speeds in urban areas as much of the Pacific
Electric trackage was in streets shared with
automobiles and trucks, and virtually all street crossings were at-grade. During the 1920s the popularity of automobiles increased and service to some communities was discontinued. Increasing automobile
traffic also led to decreasing Red Car speeds in urban areas as much of the Pacific
Electric trackage was in streets shared with
automobiles and trucks, and virtually all street crossings were at-grade.
The
Great Depression during the 1930's also caused ridership to drop. Unable to purchase new trolleys, the PE began
bus substitution in the late 30's and closed the line to Pasadena. World War
II brought a brief resurgence in popularity to rail travel, ridership numbers hit an all-time high in 1944. But by the 1950s
it was clear, however, that the automobile had become the premier means of travel in L.A. Northern District
service was discontinued in September 1951 after the PE was forced to abandon its Northern District lines near downtown
LA for construction of a new freeway.
In 1953, the Metropolitan Coach
Lines gained control of the bus lines and red car lines. Western District service ended in 1955. In 1958 the newly created
Los Angeles Metropolitan Transit Authority took over both bus and rail passenger service in southern California. The Los
Angeles to Long Beach line ceased operation on April 8, 1961.
Today the MTA
Blue Line uses much the same route that was the Pacific
Electric's route between Los Angeles and Long
Beach. There is street trackage at both the Long Beach and Los Angeles ends of the line, and a short subway section
at the Los Angeles terminus.
|
OERM Exhibits and Operates Cars from the PE Railway
 Orange
Empire Railway Museum's interurban collection includes wooden and steel
electric interurban passenger cars, electric locomotives, freight cars and
maintenance of way cars. The core of the museum's interurban railway collection
is the "Red Cars" from the Pacific Electric Railway.
Several other electric interurban railways are also represented. These cars are exhibited in Abbenseth Car House No. 2 and its yard,
Hugh Smith Car House No. 4 and its yard and elsewhere. Labels provide information about
the each car or locomotive. Orange
Empire Railway Museum's interurban collection includes wooden and steel
electric interurban passenger cars, electric locomotives, freight cars and
maintenance of way cars. The core of the museum's interurban railway collection
is the "Red Cars" from the Pacific Electric Railway.
Several other electric interurban railways are also represented. These cars are exhibited in Abbenseth Car House No. 2 and its yard,
Hugh Smith Car House No. 4 and its yard and elsewhere. Labels provide information about
the each car or locomotive.
Smaller interurban transit objects, including tokens, coin changers,
punches, uniform parts and rule books are displayed in the Middleton collection.
An interurban car is operated on the museum's mainline offering visitors
a first hand interurban experience, much like the city street car experience
provided on the Pinacate loop line. Interurban cars typically alternate
trips with a train composed of historic equipment and passenger carrying
flat cars.
|
Pardon our dust. The track gang is still working on this page.
 Photo by Richard Boehle
Photo by Richard Boehle
Entire web site copyright 2002-2009, DigitalNetExpress.com, Burbank, California.
|

